A virtual private network (VPN) extends a private network across a public network and enables users to send and receive data across shared or public networks as if their computing devices were directly connected to the private network. In other words, A Virtual Private Network is a connection method used to add security and privacy to private and public networks.
In very simple terms, a virtual private network connects your PC, smartphone, or tablet to another computer (called a server) somewhere on the internet, and allows you to browse the internet using that computer’s internet connection. So if that server is in a different country, it will appear as if you are coming from that country, and you can potentially access things that you couldn’t normally. (Source: howtogeek.com)
A virtual private network is commonly used to secure connection to public Wi-FI hotspot, hide IP address and make your browsing private. For security, the private network connection may be established using an encrypted layered tunneling protocol, and users may be required to pass various authentication methods to gain access to the virtual private network.
So, the encryption and anonymity that a virtual private network provides helps protect your online activities:
- Sending emails
- Access Geo-Blocked websites
- Shopping online
- Access a business network while traveling
- Web browsing anonymously
- Downloading files by torrent
VPNs use encryption to scramble data when it’s sent over an internet connection. Encryption makes the data unreadable. Data security is especially important when using a public Wi-Fi network, because it prevents anyone else on the network from eavesdropping on your internet activity.
Privacy is very important for us. Without a VPN, your internet service provider can know your entire browsing history. With a virtual private network, your search history is hidden. That’s because your web activity will be associated with the VPN server’s IP address, not yours. A virtual private network service provider may have servers all over the world. That means your search activity could appear to originate at any one of them.
A virtual private network can hide a lot of information that can put your privacy at risk:
- Web browsing history
- IP address and location
- Location for streaming
- Device type and device information
- Web activity — to maintain internet freedom
Source: norton.com
Who Can Benefit from a VPN?
- Privacy geeks
- Security devotees
- Sports zealots
- Human rights activists
- Travelers
- Avid gamers
- Movie & TV show fans
- Torrenting enthusiasts
- Mobile users
Source: surfshark.com
Security
VPNs use advanced encryption protocols and secure tunneling techniques to encapsulate all online data transfers. Evolving security threats and ever increasing reliance on the Internet make a Virtual Private Network an essential part of well-rounded security. Integrity checks ensure no lost data and the connection not hijacked. To prevent disclosure of private information, virtual private networks typically allow only authenticated remote access using tunneling protocols and encryption techniques.
The VPN security model provides:
- Confidentiality: Even if the network traffic is sniffed at the packet level, an attacker would see only encrypted data sender authentication to prevent unauthorized users from accessing the VPN message integrity to detect any instances of tampering with transmitted messages.
- Authentication: Tunnel endpoints must be authenticated before secure VPN tunnels can be established. User-created remote-access VPNs may use passwords, biometrics, two-factor authentication or other cryptographic methods.
Secure VPN protocols include the following:
- IPsec: This protocol uses encryption, encapsulating an IP packet inside an IPsec packet. De-encapsulation happens at the end of the tunnel, where the original IP packet is decrypted and forwarded to its intended destination. Read more here about IPsec.
- SSL/TLS: These protocols can tunnel an entire network’s traffic or secure an individual connection. A number of vendors provide remote-access VPN capabilities through SSL. An SSL VPN can connect from locations where IPsec runs into trouble with Network Address Translation and firewall rules. Read more here about SSL/TLS.
- Datagram Transport Layer Security (DTLS): This protocol used in Cisco AnyConnect VPN and in OpenConnect VPN to solve the issues SSL/TLS has with tunneling over TCP.
- Microsoft Point-to-Point Encryption (MPPE): This protocol works with the Point-to-Point Tunneling Protocol and in several compatible implementations on other platforms.
- Microsoft Secure Socket Tunneling Protocol (SSTP): this protocol tunnels Point-to-Point Protocol (PPP) or Layer 2 Tunneling Protocol traffic through an SSL/TLS channel.
- Secure Shell (SSH) VPN: OpenSSH offers VPN tunneling to secure remote connections to a network or to inter-network links. OpenSSH server provides a limited number of concurrent tunnels. The VPN feature itself does not support personal authentication.
- WireGuard: This new protocol supports was added to both the Linux and Android kernels, opening it up to adoption by VPN providers.
Source: en.wikipedia.org
Site-to-site
A Site-to-Site VPN is also called as Router-to-Router VPN and is mostly used in the corporates. Companies, with offices in different geographical locations, use Site-to-site VPN to connect the network of one office location to the network at another office location.
- Intranet based VPN: When multiple offices of the same company are connected using Site-to-Site VPN type.
- Extranet based VPN: When companies use Site-to-site VPN type to connect to the office of another company.
Basically, Site-to-site creates a virtual bridge between the networks at geographically distant offices and connect them through the Internet and maintain a secure and private communication between the networks.
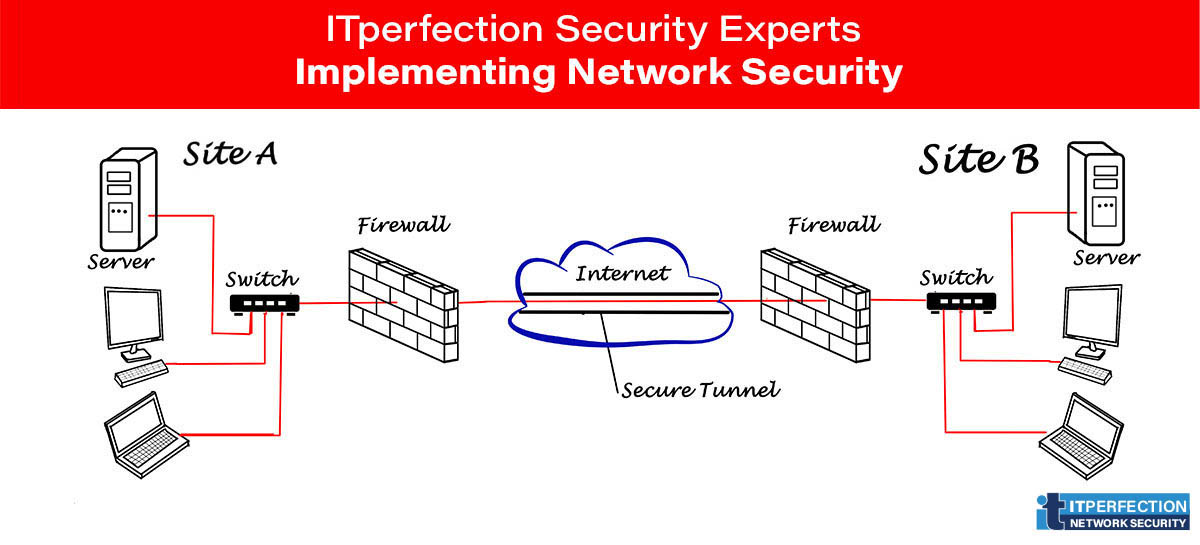
Anyway, in this VPN type one router acts as a virtual private network Client and another router as a VPN Server. The communication between the two routers starts only after an authentication is validated between the two. (Source: vpnoneclick.com)
Remote Access
Remote access VPN allows a user to connect to a private network and access its services and resources remotely. The connection between the user and the private network happens through the Internet and the connection is secure and private. A corporate employee, while traveling, uses a virtual private network to connect to his/her company’s private network and remotely access files and resources on the private network.
Home users, or private users of virtual private network, primarily use VPN services to bypass regional restrictions on the Internet and access blocked websites. Users conscious of Internet security also use VPN services to enhance their Internet security and privacy. (Source: vpnoneclick.com)
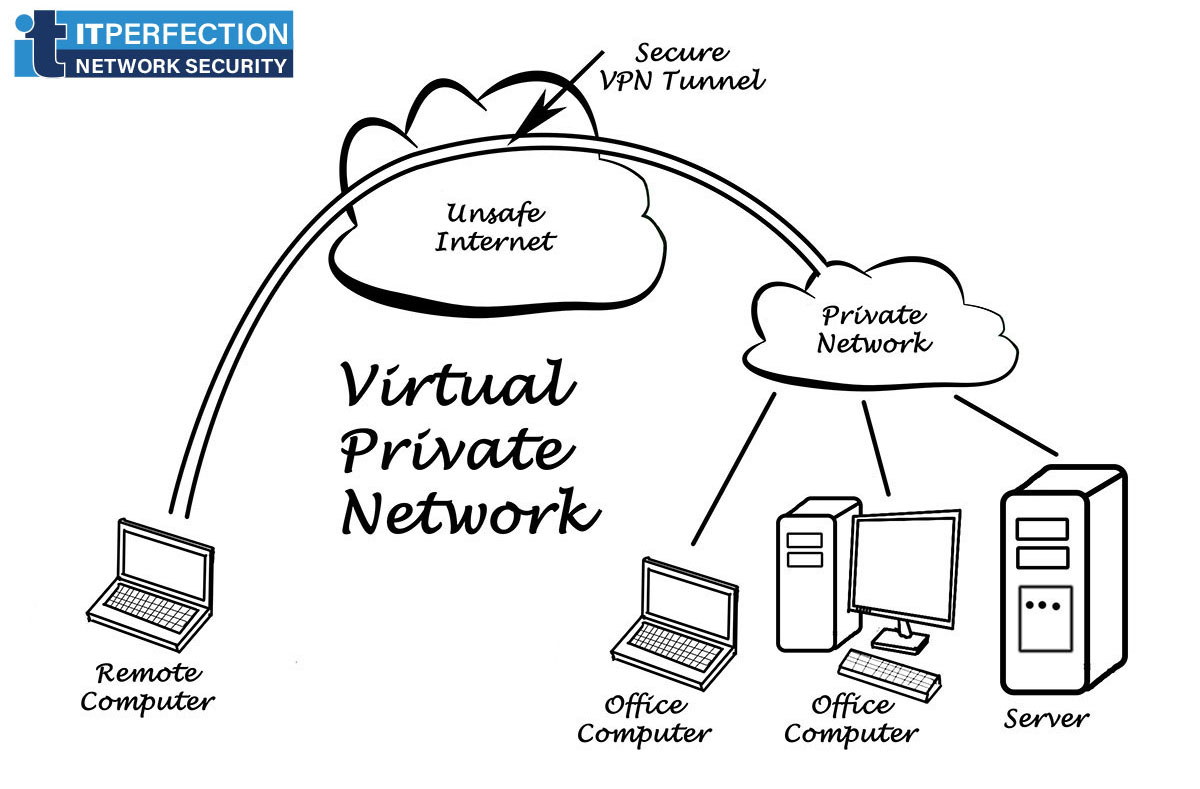
The main benefits of remote access VPNs are easy setups and hassle-free use. With the right software, this type of VPN can be easily accessible to newcomers and veterans alike, and is ideal for personal use. However, it may be unsuitable for (and even incompatible with) large-scale business needs. (Source: vpnmentor.com)
———————————
Sources:


















