In this post we are going to talk about Physical Safeguards. This post is the third post in the HIPAA series. This series of posts is called the HIPAA Series.
The series will contain seven post:
- Security 101 for Covered Entities
- Security Standards: Administrative Safeguards
- Security Standards: Physical Safeguards
- Security Standards: technical Safeguards
- Security Standards- Organizational, Policies and Procedures and Documentation Requirements
- Basics of Risk Analysis and Risk Management
- Implementation for the Small Provider
But this series also has two spin offs. We suggest that if you do not have basic information about HIPAA, before starting this series, first read the following two posts:
Note, In across of this post:
(R)= Required, (A)= Addressable
—————————–
Source:
This article is a summary from of the hhs.gov website. With the following link:
Security Standards: Physical Safeguards
For more info please refer to hhs.gov
Physical Safeguards
The Security Rule defines physical safeguards as “physical measures, policies, and procedures to protect a covered entity’s electronic information systems and related buildings and equipment, from natural and environmental hazards, and unauthorized intrusion.”
So, a covered entity must consider all physical access to EPHI. This may extend outside of an actual office, and could include workforce members’ homes or other physical locations where they access EPHI.
Physical Safeguards includes four standards, all of which we will discuss. These standards include:

Facility Access Controls – STANDARD § 164.310(a) (1)
The first standard under the Physical Safeguards section is Facility Access control. It requires covered entities to: “Implement policies and procedures to limit physical access to its electronic information systems and the facility or facilities in which they are housed, while ensuring that properly authorized access is allowed.”

Contingency Operations (A)
The Contingency Operations implementation specification refers to physical security measures entities establish in the event of the activation of contingency plans and employ while the contingency plans required by the Administrative Safeguards are active. The covered entity must: “Establish (and implement as needed) procedures that allow facility access in support of restoration of lost data under the disaster recovery plan and emergency mode operations plan in the event of an emergency.”
Contingency operations may be set in motion during or immediately following a disaster or emergency situation.
Facility Security Plan (A)
The Facility Security Plan defines and documents the safeguards used by the covered entity to protect the facility or facilities. So, a covered entity must: “Implement policies and procedures to safeguard the facility and the equipment therein from unauthorized physical access, tampering, and theft.”
Facility security plans must document the use of physical access controls, and these controls must ensure that only authorized individuals have access to facilities and equipment that contain EPHI.
To establish the facility security plan, covered entities should review risk analysis data on persons or workforce members that need access to facilities and equipment. This includes staff, patients, visitors and business partners.
Some common controls include:
- Locked doors, signs warning of restricted areas, surveillance cameras, alarms
- Property controls such as property control tags, engraving on equipment
- Personnel controls such as identification badges, visitor badges and/or escorts for large offices
- Private security service or patrol for the facility

Access Control and Validation Procedures (A)
The covered entity must: “Implement procedures to control and validate a person’s access to facilities based on their role or function, including visitor control, and control of access to software programs for testing and revision.”
These functional or role-based access control and validation procedures should be closely aligned with the facility security plan. These procedures are the means by which a covered entity will actually determine the workforce members or persons that should have access to certain locations within the facility based on their role or function.
The controls implemented will depend on the covered entity’s environmental characteristics. In a large organization, because of the number of visitors and employees, this practice may be required for every visit. In a small doctor’s office, once someone’s identity has been verified it may not be necessary to check identity every time he or she visits, because the identity would already be known.

Maintenance Records (A)
The Maintenance Records implementation specification requires that covered entities document such repairs and changes. The covered entity must:
“Implement policies and procedures to document repairs and modifications to the physical components of a facility which are related to security (for example, hardware, walls, doors and locks).”
In a small office, documentation may simply be a logbook that notes the date, reason for repair or modification and who authorized it. In a large organization, various repairs and modifications of physical security components may need to be documented in more detail and maintained in a database.

Workstation Use – STANDARD § 164.310 (b)
This standard has no implementation specifications, but like all standards must be implemented.
A workstation is defined in the rule as “an electronic computing device, for example, a laptop or desktop computer, or any other device that performs similar functions, and electronic media stored in its immediate environment.”
Inappropriate use of computer workstations can expose a covered entity to risks, such as virus attacks, compromise of information systems, and breaches of confidentiality.
For this standard, covered entities must: “Implement policies and procedures that specify the proper functions to be performed, the manner in which those functions are to be performed, and the physical attributes of the surroundings of a specific workstation or class of workstation that can access electronic protected health information.”
Covered entities must assess their physical surroundings to ensure that any risks associated with a workstation’s surroundings are known and analyzed for a possible negative impact.
The Workstation Use standard also applies to covered entities with workforce members that work off site using workstations that can access EPHI. This includes employees who work from home, in satellite offices, or in another facility. Workstation policies and procedures must specify the proper functions to be performed, regardless of where the workstation is located.

Workstation Security – STANDARD § 164.310 (c)
It is a standard with no implementation specifications. Workstation Security standard addresses how workstations are to be physically protected from unauthorized users. This standard requires that covered entities: “Implement physical safeguards for all workstations that access electronic protected health information, to restrict access to authorized users.”
One way may be to completely restrict physical access to the workstation by keeping it in a secure room where only authorized personnel work.

Device and Media Controls – STANDARD § 164.310(d) (1)
The Device and Media Controls standard requires covered entities to: “Implement policies and procedures that govern the receipt and removal of hardware and electronic media that contain electronic protected health information, into and out of a facility, and the movement of these items within the facility.”
The term “electronic media” means, “electronic storage media including memory devices in computers (hard drives) and any removable/transportable digital memory medium, such as magnetic tape or disk, optical disk, or digital memory card…”
Disposal (R)
The Disposal implementation specification states that covered entities must: “Implement policies and procedures to address the final disposition of electronic protected health information, and/or the hardware or electronic media on which it is stored.”
When covered entities dispose of any electronic media that contains EPHI they should make sure it is unusable and/or inaccessible.
There are two common way to dispose of electronic media:
- Degaussing: It is a method whereby a strong magnetic field is applied to magnetic media to fully erase the data.
- Inflicting physical damage to the electronic media and making the data inaccessible.

Media Re-use (R)
Instead of disposing of electronic media, covered entities may want to reuse it. Media Re-Use, a required implementation specification for this standard, states that covered entities must: “Implement procedures for removal of electronic protected health information from electronic media before the media are made available for re-use.”
- Internal re-use may include re-deployment of PCs or sharing floppy disks.
- External re-use may include donation of electronic media to charity organizations or local schools.
Anyway, it is important to remove all EPHI previously stored on the media to prevent unauthorized access to the information.

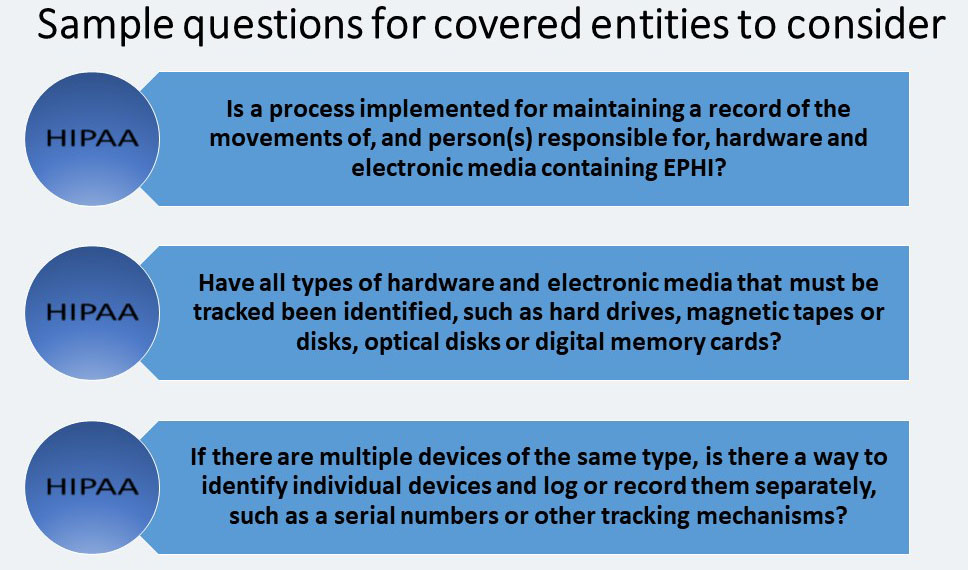
Accountability (A)
Portable workstations and media present a special accountability challenge. Since this is an addressable specification, each covered entity must determine if and how it should be implemented for their organization. The covered entity must: “Maintain a record of the movements of hardware and electronic media and any person responsible therefore.”
If a covered entity’s hardware and media containing EPHI are moved from one location to another, a record should be maintained as documentation of the move.
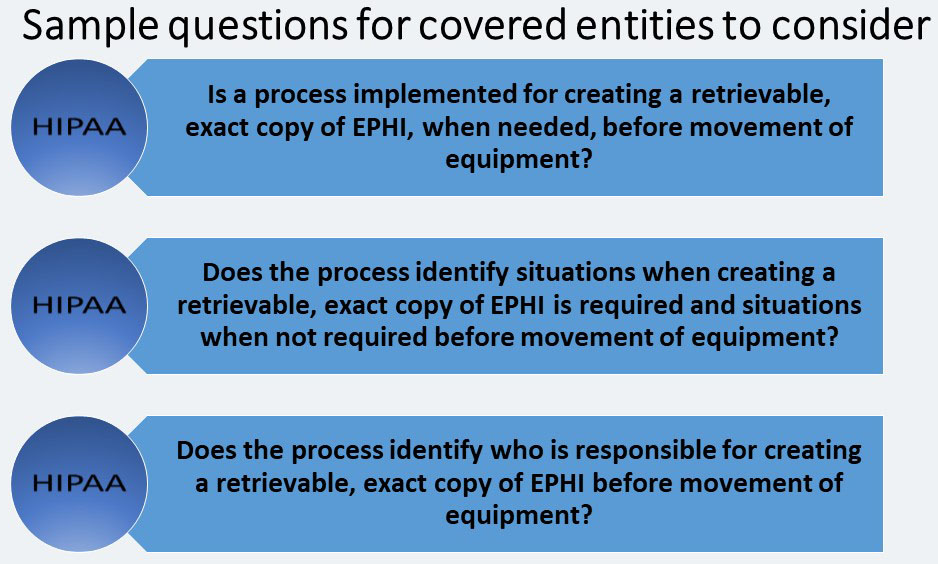
Data Backup and Storage (A)
A covered entity must: “Create a retrievable, exact copy of electronic protected health information, when needed, before movement of equipment.”
This specification protects the availability of EPHI and is similar to the Data Backup Plan implementation specification for the contingency plan standard of the Administrative Safeguards. Therefore, both implementation specifications may be included in the same policies and procedures.
Larger organizations may implement policies that require users to save all information on the network, thus eliminating the need for a hard drive back up prior to the move.
—————————–
Source:
This article is a summary from of the hhs.gov website. With the following link:
Security Standards: Physical Safeguards
For more info please refer to hhs.gov



















