The subject of this post is to review the privacy settings as well as security settings in the popular google chrome web browser. This web browser provides many settings in these two areas for its users, the most important of which we examine.
To enter the privacy settings as well as security settings you must:
- Click on the three-dot (vertical) icon in the upper right corner of the browser.
- In the menu that appears, click on Settings.
3- A page like the following figure appears:
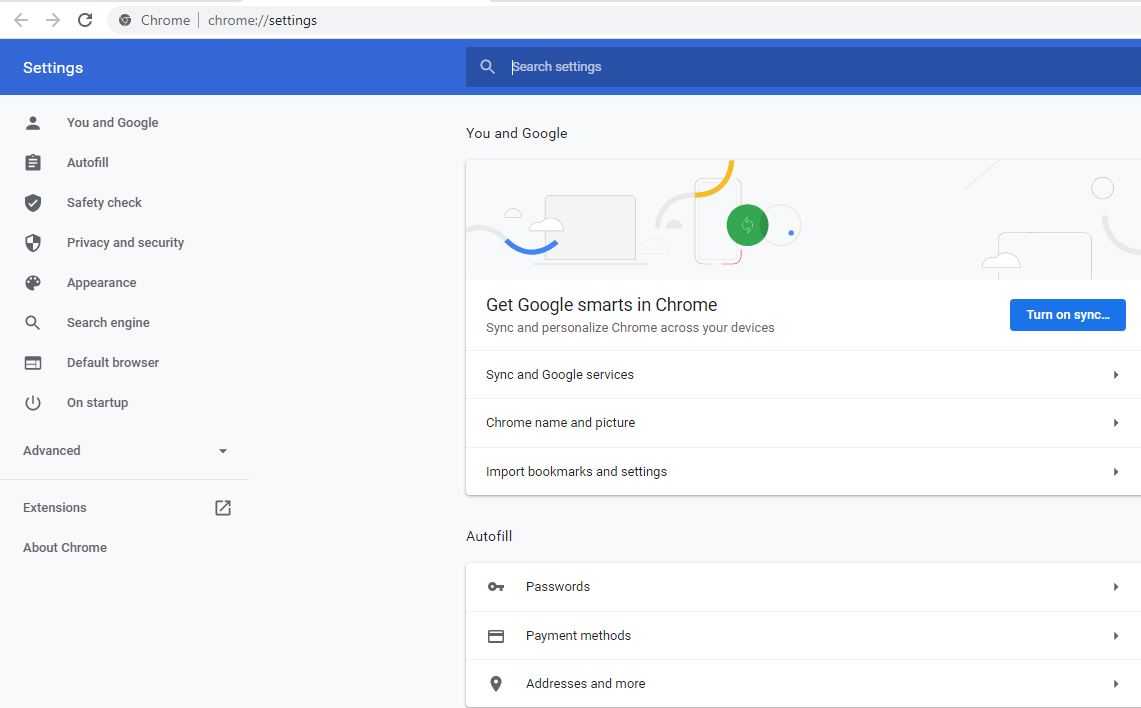
4- Click on Privacy and Security in left pane. You will now be redirected to the settings section. Figure below:
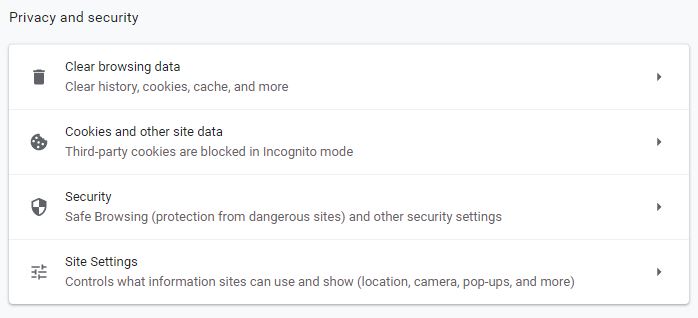
As you can see, there are four general sections:
- Clear browsing data: For clearing history, cookies, cache, and more.
- Cookies and other site data: For third-party cookies management.
- Security: This section includes safe browsing options and also other security settings.
- Site settings: To control the content allowed to be displayed and used.

Click the arrow icon in the right corner to display the settings for this section:
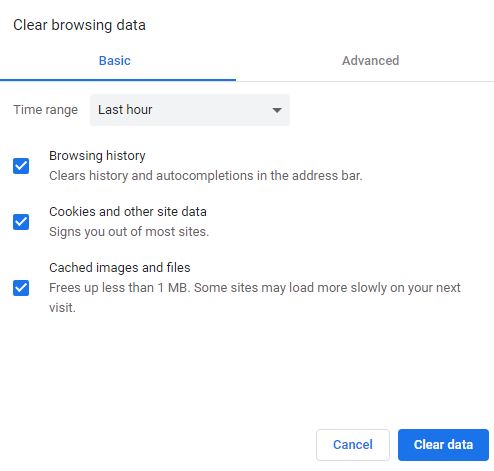
This window includes two tab: Basic and Advanced.
In both tabs, there is a Time range menu:
- Last hour
- Last 24 hours
- Last 7 day
- Last 4 Weeks
- All time.
You must choose one of these time ranges.
There are three options in Basic tab:
- Browsing history: You can select this option so that the URLs you have visited (within the time period you specify) are removed from the browser history and no longer appear in the address bar.
- Cookies and other site data: What’s cookie? Cookies are usually small text files that are stored on your computer’s browser directory or program data subfolders. Cookies are created when you use your browser to visit a website that uses cookies to keep track of your movements within the site, help you resume where you left off, remember your registered login, and other customization functions. There are two types of cookies: session cookies and persistent cookies. Session cookies are created temporarily in your browser’s subfolder while you are visiting a website. Once you leave the site, the session cookie is deleted. Persistent cookie files remain in your browser’s subfolder and are activated again once you visit the website that created that particular cookie. Anyway, you can select this option to signs you out of most sites.
- Cached images and files: When you first visit a website, the browser automatically (and by default) caches the files (including images) of the website. What is the benefit of this? Simply put, this will make the website load faster the next time you visit it. It is a great capability, but you should note that these files are stored on the computer hard drive and after a while these files will take up a lot of space. By selecting this option, you can delete the cached files and free up the space. Of course, some sites load more slowly on your next visit.
The Advanced tab contains the three options you saw, as well as a number of other options.
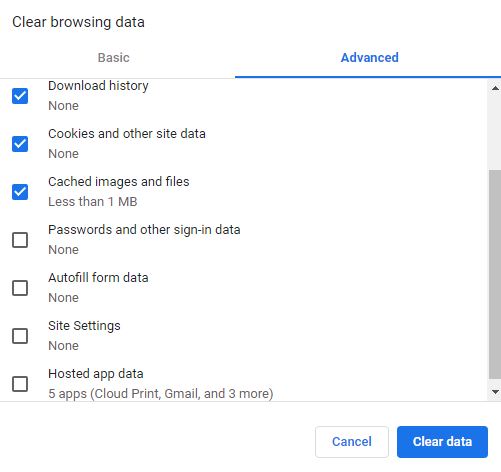
Special options for this tab are:
- Download history: You can select this option to delete the history of files downloaded by the browser. Note that the files themselves will not be deleted. Instead, the history of information related to the download operation (the host site of that file, the file name in the above website, etc.) will be deleted.
- Passwords and other sign-in data: By default, if you enter a new password on a site, Chrome will ask to save it. How Chrome saves your passwords depends on whether you want to store and use them across devices. When synced, passwords can be used on Chrome on all your devices, and across some apps on your Android devices. By selecting this option, you can delete all saved passwords.
- Autofill form data: One of the perks of using Google Chrome is the ability to sync your autofill data such as your address and credit card number between all of your devices. By selecting this option, you can delete all these data.
- Site settings: By selecting this options, you delete all stored settings of websites.
- Hosted app data: These data refers to data from the apps you’ve added to Chrome from the Chrome Web Store. For example, the local storage used by Gmail Offline. You can delete these data by selecting this option.
Anyway, when you have selected the items you want to delete, then click the Clear data button.

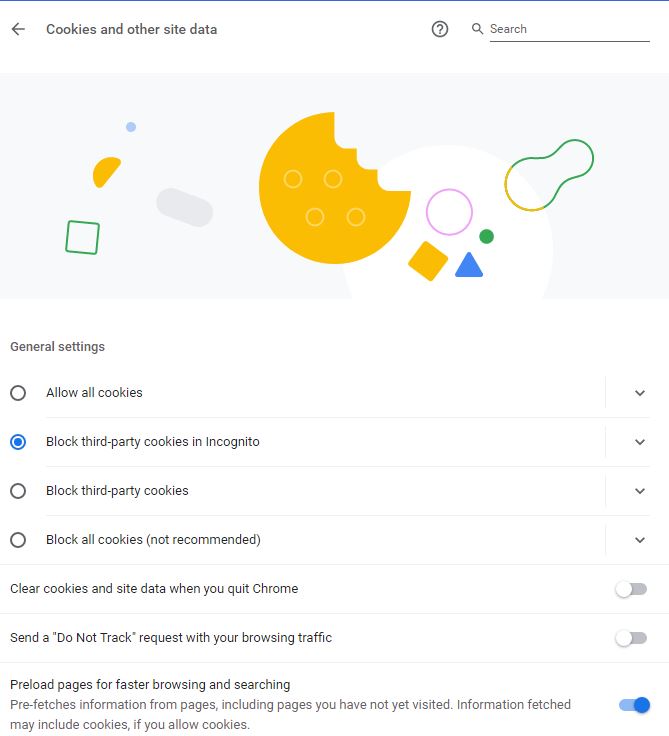
General settings contains four radio button:
- Allow all cookies: If you select this option, then sites can use cookies to improve your browsing experience. Also, sites can use cookies to see your browsing activity across different sites, for example, to personalize ads.
- Block third-party cookies in Incognito: If you select this option, sites can’t use your cookies to see your browsing activity across different sites, for example, to personalize ads. Features on some sites may break. This option selected by default.
- Block third-party cookies: If you select this option, sites can’t use your cookies to see your browsing activity across different sites, for example, to personalize ads. Features on some sites may break.
- Block all cookies: If you can select this option, none of the Sites can’t use cookies to improve your browsing experience. Sites can’t use your cookies to see your browsing activity across different sites, for example, to personalize ads. Features on many sites may break.
Clear cookies and site data when you quit Chrome: Enable this option if you do not want cookies to be stored permanently.
Send a “Do Not Track” request with your browsing traffic: Enabling “Do Not Track” means that a request will be included with your browsing traffic. Any effect depends on whether a website responds to the request, and how the request is interpreted. For example, some websites may respond to this request by showing you ads that aren’t based on other websites you’ve visited. Many websites will still collect and use your browsing data – for example to improve security, to provide content, services, ads and recommendations on their websites, and to generate reporting statistics.
At the end of the settings of this section you can:
- Add sites that can always use cookies.
- Add always clear cookies when windows are closed.
- Add Sites that can never use cookies.

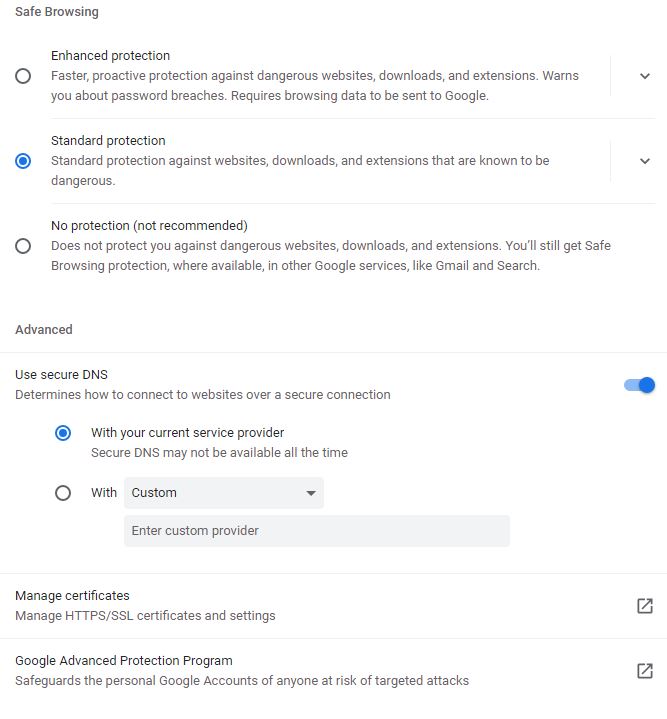
Safe browsing
Safe Browsing protects you against attackers who may trick you into doing something dangerous like installing malicious software or revealing personal information like passwords, phone numbers, or credit cards.
This capability has three radio button:
Enhanced protection: This option Predicts and warns you about dangerous events before they happen. Also it Keeps you safe on Chrome and may be used to improve your security in other Google apps when you are signed in. Enhanced protection Improves security for you and everyone on the web, and it warns you if passwords are exposed in a data breach. Finally, this option sends URLs to Safe Browsing to check them. Also sends a small sample of pages, downloads, extension activity, and system information to help discover new threats. Temporarily links this data to your Google Account when you’re signed in, to protect you across Google apps.
- Standard protection: It’s default selection. This option enables a protection against websites, downloads, and extensions that are known to be dangerous. This option detects and warns you about dangerous events when they happen. Also, it Checks URLs with a list of unsafe sites stored in Chrome. If a site tries to steal your password, or when you download a harmful file, Chrome may also send URLs, including bits of page content, to Safe Browsing.
- No protection: This option does not protect you against dangerous websites, downloads, and extensions. Of course, you’ll still get Safe Browsing protection, where available, in other Google services, like Gmail and Search.
Standard protection contains two other options that they aren’t enable by default:
- Help improve security on the web for everyone: If you enable this option, then chrome sends URLs of some pages you visit, limited system information, and some page content to Google, to help discover new threats and protect everyone on the web.
- Warn you if passwords are exposed in a data breach: It’s recommend you enable this option. Chrome periodically checks your passwords against lists that have been published online. When doing this, your passwords and usernames are encrypted, so they can’t be read by anyone, including Google.
Use secure DNS
In general, what’s secure DNS? It’s better you read this article:
Secure Domain Name System (DNS) Deployment Guide ) NIST Special Publication 800-81-2, Ramaswamy Chandramouli Scott Rose (
This feature determines how to connect to websites over a secure connection, and it include two modes:
With your current service provider: Secure DNS may not be available all the time.
With other service providers: There are some options.
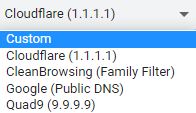
You must select one of them, or enter a custom address.
Manage certificates
You can manage HTTPS/SSL certificates and settings in this section.

You can control what information sites can use and show (location, camera, pop-ups, and more).
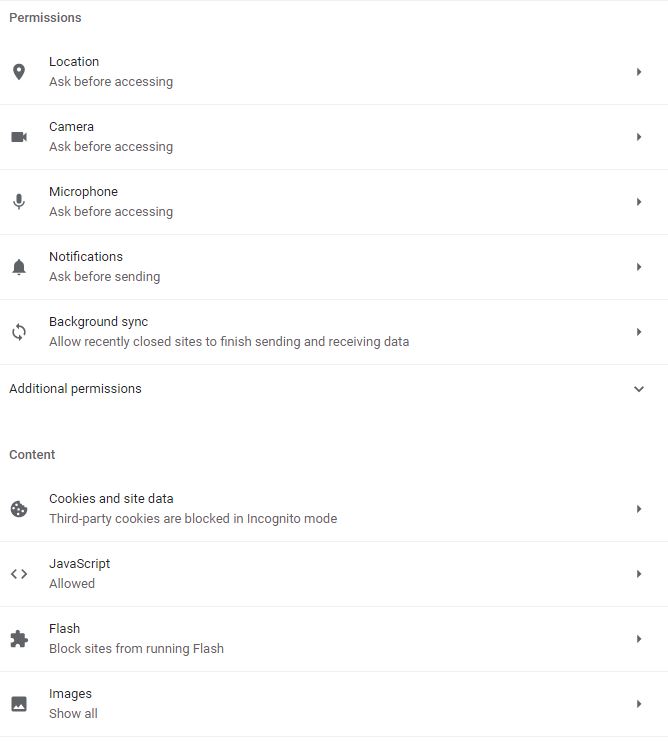
Location
In this section, you can specify that websites must ask you a question before accessing the location information, and only if your answer is yes, then websites accesses the location information.
You can also specify two categories of websites in this section:
- Allow mode: Websites that should always have access to location information – without the need to ask questions.
- Block mode: Websites that should never have access to location information.
Camera
In this section, you can specify that websites must ask you a question before accessing to camera, and only if your answer is yes, then websites accesses it.
You can also specify two categories of websites in this section:
- Allow mode: Websites that should always have access to camera – without the need to ask questions.
- Block mode: Websites that should never have access to camera.
Microphone
In this section, you can specify that websites must ask you a question before accessing to microphone, and only if your answer is yes, then websites accesses it it.
You can also specify two categories of websites in this section:
- Allow mode: Websites that should always have access to microphone – without the need to ask questions.
- Block mode: Websites that should never have access to microphone.
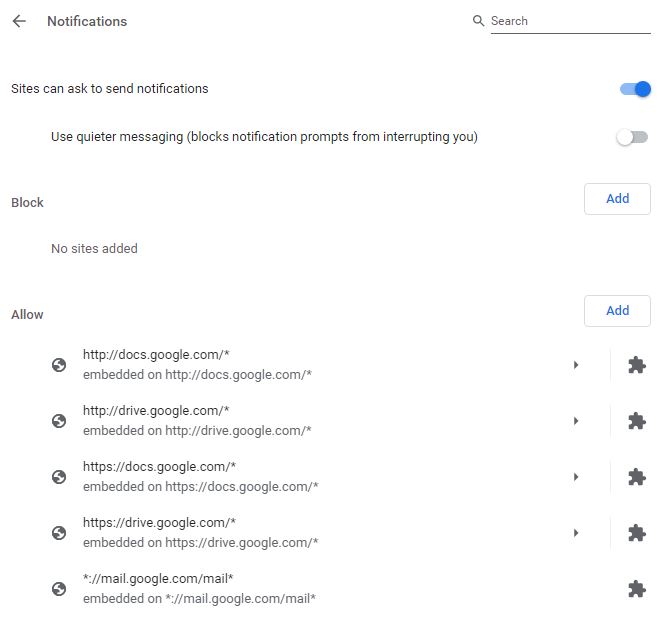
Notifications
In this section, you can specify whether websites can issue notifications for your browser?
You can also specify two categories of websites in this section:
- Websites that are allowed to notifications.
- Those that should not be allowed.
Background sync
You can allow recently closed sites to finish sending and receiving data in this section.
Motion sensors
For allowing/blocking sites to use motion sensors.
Automatic downloads
Ask when a site tries to download files automatically after the first file.
In this section you can also specify from which sites the browser is allowed to download the file automatically (without the need to ask questions) and from which websites it should never download the file.
And other permissions and content settings
Similar to the previous few items, in this section of the browser security settings window, you can set permissions for the following:
- Unsandboxed plugin access
- Handlers
- MIDI devices
- USB devices
- Serial ports
- File editing
- Clipboard
- Payment Handlers
- Augmented reality
- Virtual Reality
- Cookies and site data
- Java scripts
- Flash files
- Images
- Pop-ups and redirects
- Sound
- Ads
- Zoom levels
- PDF documents
- Protected content
- Insecure content

Start or stop saving passwords
1- Open Chrome.
2- At the top right, click Profile and then Passwords.
3- Turn Offer to save passwords on or off.
Enabling/disabling autofill forms
1- Open Chrome.
2- In settings window, select Autofill in left pane.
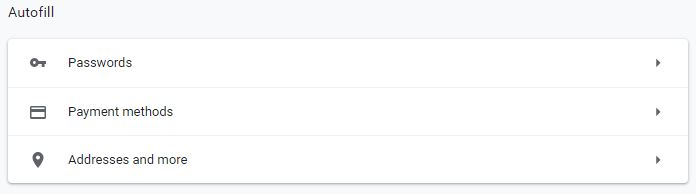
3- From each of these menus, you can choose to enable or disable the option to autofill forms on web pages. To do this, just toggle the item on or off.
In passwords:
- Offer to save passwords
- Auto Sign-in: Automatically sign in to websites using stored credentials. If disabled, you will be asked for confirmation every time before signing in to a website.
In Payment methods:
- Save and fill payment methods: Fills in payment forms with your saved payment methods.
- Allow sites to check if you have payment methods saved.
In Addresses and more:
- Save and fill addresses: It includes information like phone numbers, email addresses, and shipping addresses.



















