Monitoring system resources is a necessary part of troubleshooting. Resources include memory, mass storage, network access, processor power, and so on. Computer hardware and software resources must be managed. Proper management is not possible without resources monitoring. In this post, we’ll take a look at resources monitoring and also task manager window to help you understand the different aspects of these resources monitoring on a computer with Microsoft Windows OS.
The biggest problem in Windows is that there are way too many utilities to choose from when you’re trying to track resources. The most prominent one is probably the Windows Task Manager, as it highlights resource usage of individual processes, and gives admins and users options to kill any misbehaving ones. So, Summon the Task Manager by pressing Ctrl+Shift+Esc.
Task Manager has differences in different versions of Windows. We will describe the general aspects of this console in windows 10.
Source: dummies.com and howtogeek.com
Task Manager Overview
By default, in Windows 10, you’ll see the slimmed down version, which just gives you a list of running applications.
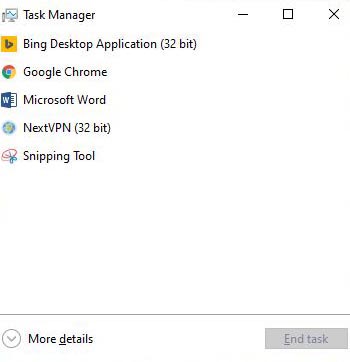
To close a program in this version, click on it and click on End Task button. For seen more details, click on More details. This will bring up the task manager with all the tabs.
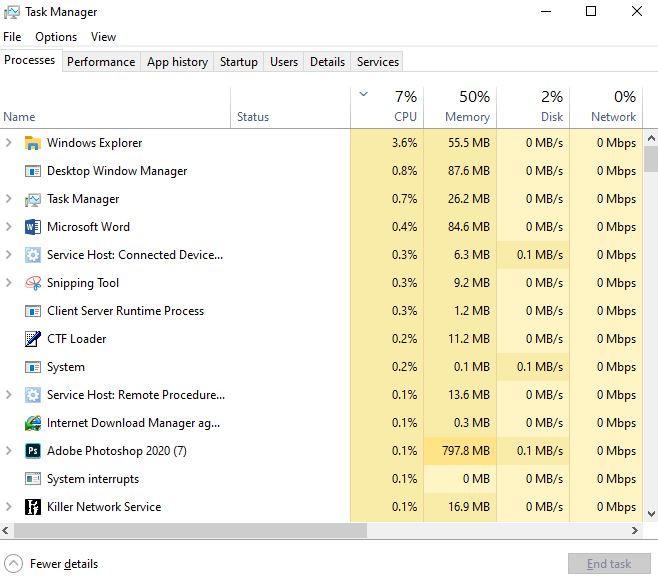
In this version, there are seven tab:
- Process: This tab will list all processes (and applications) that are running on the system. Some processes may be running on the background. Of course, in some versions of the Windows operating system and in the task manager console, the processes and applications each have their own tab.
- Performance: This tab include real-time information about the system resources (such as information about CPU and Memory usage).
- App history: This tab collects and reports usage statistics for the apps and programs running on your computer or device over the last month.
- Startup: In addition to the monitoring aspect, this tab also has a settings aspect. In this tab, you can specify which applications to run on startup and which applications not to run.
- Users: This tab shows online users and it lets you view which user accounts are logged in and also see how much of the computer’s resources are being used to keep them online. This tab also lets you close the apps opened by other users or even log them out.
- Details: This tab provides a solid base of information about the processes currently running on your system.
- Services: Here we can see which services are currently running on the computer and which services are stopped.
Source: digitalcitizen.life and howtogeek.com
Process Tab
This tab will list all processes (and applications) that are running on the system. The list of processes is broken down into three main categories:
- Apps: list of all the currently running programs on PC
- Background processes: All Windows Store apps and third-party apps running on the system. Some of the processes here you might see running in the system tray.
- Windows processes (or System processes): We have published a special post about windows processes. It is better to read it.
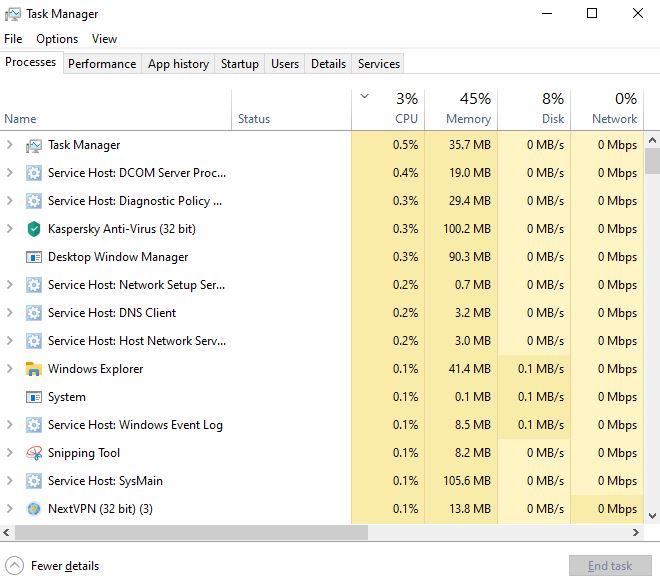
This tab has some columns:
- CPU
- Memory
- Disk (Hard Disk)
- Network (network’s bandwidth)
- GPU (Graphic Processor Unit)
These columns show each process or each application uses how much of each of these hardware resources. For example, a process may be using hardware resources as follows:
5% of the CPU
100 MB of memory (RAM)
85 MB of disk
2 Mbps of network bandwidth
8 percent of the GPU
Task Manager Displays active processes and lets you end most items by clicking End Process. You can also customize Task Manager to increase or decrease the level of detail shown on the Processes tab. This tab consists of all the core processes that are needed for Windows 10 to run properly. It mostly consists of many Service Host (svchost.exe) processes. When you right-click on a process, you’ll get a list of actions you can perform on that process.
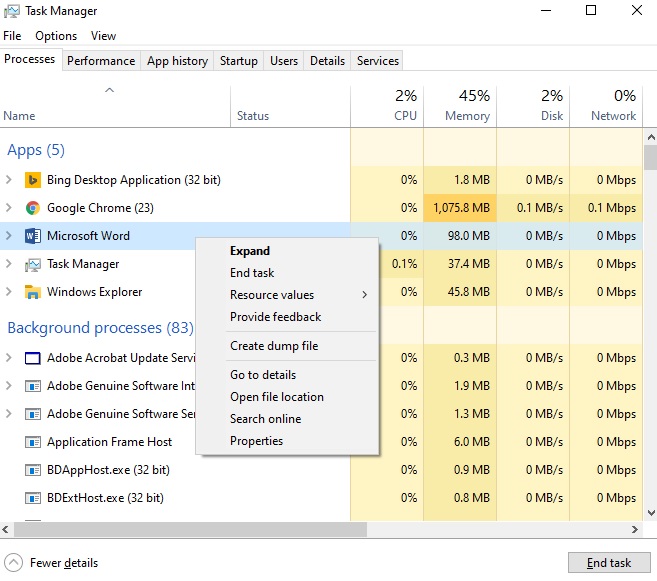
Let’s take a look at the options in this context menu:
- Expand: To view all instances of this process or application running (for example, to see all open files belong to Microsoft Word).
- End Task: To terminate this application or process.
- Resource values: This option has three other options called memory, disk and network. With this option, you can specify how to display the use of the above resources by any program or process: by value or by percent. By default, it is by value. Note that for the CPU and GPU, this option (resource values) has no choice and they are display only by percent.
- Provide feedback: To send feedback on the problem of this process or application or also to send a suggestion about the same process or application to Microsoft.
- Create dump file: A dump file is a debugging tool for programmers. It takes a snapshot of all the stuff that that program has stored in RAM and writes it to a file on disk. So, create dump file is only used by developers.
- Go to details: If you click on this option, you will be redirect details tab for this process (you will read about the above tab soon).
- Open file location: This option is useful if you want to know the location of the EXE file on your computer.
- Search online: Searching in the internet for this process or program.
- Properties: This option display properties of the process or program. Like the following figure:
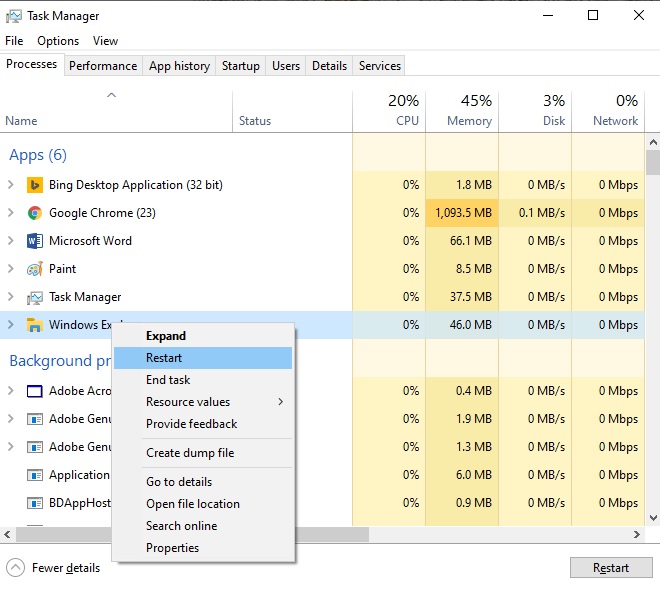
The Processes tab is also good for restarting Explorer. All you have to do is right-click on Windows Explorer and choose Restart.
Source: online-tech-tips.com and howtogeek.com
Performance Tab
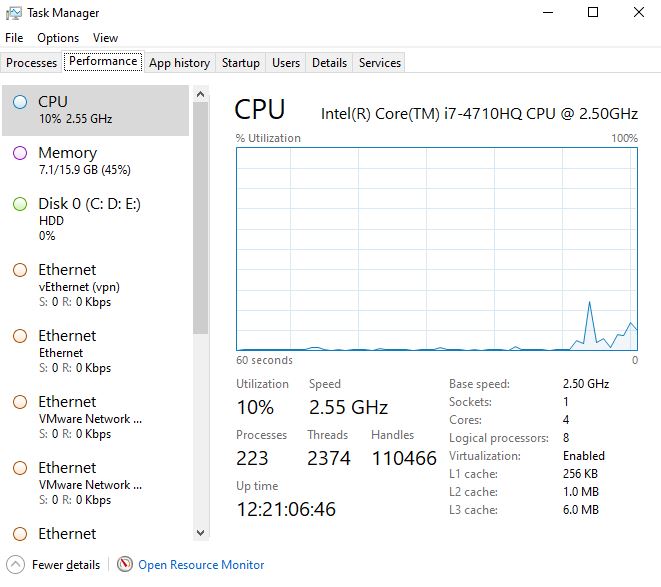
Task Manager provides data and graphs that show you detailed information on the current activity of the CPU, memory, disks, and your Ethernet/Wi-Fi connections. . There are the following information:
- CPU Utilization: Shows the current Overall utilization of the CPU, which should match where the data line meets the graph’s y-axis, on the far right.
- CPU Threads: The total number of threads running in the processes at this time.
- CPU Process: A total count of all processes running at the moment
- CPU Speed: Shows the speed at which the CPU is operating at right now
- CPU Uptime: The amount of time the processor is running (by clock)
- Memory: It includes the amount of memory that is being used currently, the amount of memory that is free currently, the frequency of the memory card and its type, the number of slots under the load and….
- Each Ethernet Usages: It include Send data rate, receive data rate, IPv4 address, IPv6 address. When you select a network adapter, you’ll notice the name of your Wi-Fi or Ethernet adapter in the top-right corner.
- Disk Usage: It include Disk capacity, disk formatted, disk page file status (yes or no), disk type (like HDD or SSD), disk average response time, read speed and write speed.
Source: sourcedaddy.com and howtogeek.com
App History Tab
This tab collects and reports usage statistics for the apps and programs running on your computer or device over the last month.
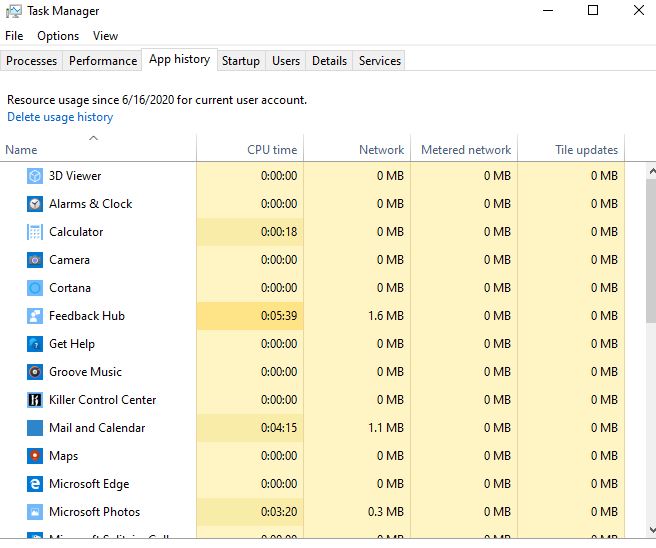
Windows 10 includes many built-in Windows Store apps and this tab will show you info about those apps and any that you install yourself. This tab is useful only to see which apps are using the most CPU or the most network bandwidth over time.
Source: digitalcitizen.life and online-tech-tips.com
Startup Tab
One of the most important tabs in the Windows 10 task manager is the Startup tab. In addition to the monitoring aspect, this tab also has a settings aspect. In this tab, you can specify which applications to run on startup and which applications not to run.
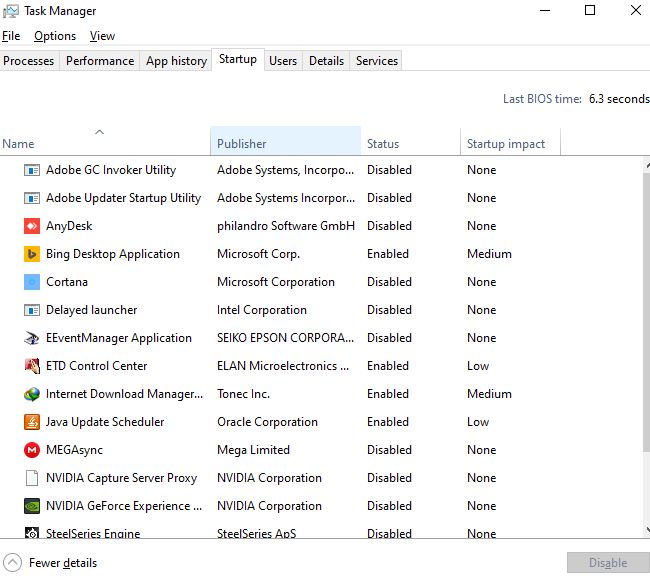
At the top and to the right, you’ll see the Last BIOS time, which will tell you exactly how long your system was in the BIOS phase before Windows loaded.
In startup impact column, you’ll find a list of all the startup items on your Windows 10 system. By default, it’s sorted alphabetically. Windows comes up with a score ranging from Low to High based on several different factors.
To disable a startup item, in status column, right-click on it and choose Disable.
Source: howtogeek.com and online-tech-tips.com
Users Tab
This tab shows online users and it lets you view which user accounts are logged in and also see how much of the computer’s resources are being used to keep them online. This tab also lets you close the apps opened by other users or even log them out. By default, you see six or seven columns displayed near the User column. They are:
- Status: shows the status of the accounts and processes listed.
- CPU: displays the percentage of total CPU cycles used by each account, and the processes run by each account.
- Memory: shows the total amount of memory the selected account (or the chosen process) is utilizing.
- Disk: indicates the amount of data being transferred to/from hard drive.
- Network: displays the network usage of the selected user account or process.
- GPU: shows the highest video utilization across all the graphics chips or cards on your PC.
- GPU engine: if you have more than one video card installed (like on a laptop with a dedicated video card but also a video chip found on the processor), GPU engine shows the utilization of the dedicated graphics card.
Source: howtogeek.com and online-tech-tips.com
Details Tab
This tab provides a solid base of information about the processes currently running on your system. Each process has an identifier. It called Process ID (PID).
In this tab, you can see the PID of each process, you can also see what status that process is in (suspended or running). Similarly, it can be seen by which user account each process is running (including system accounts).
When you right-click on a process, you’ll get a list of actions you can perform on that process.
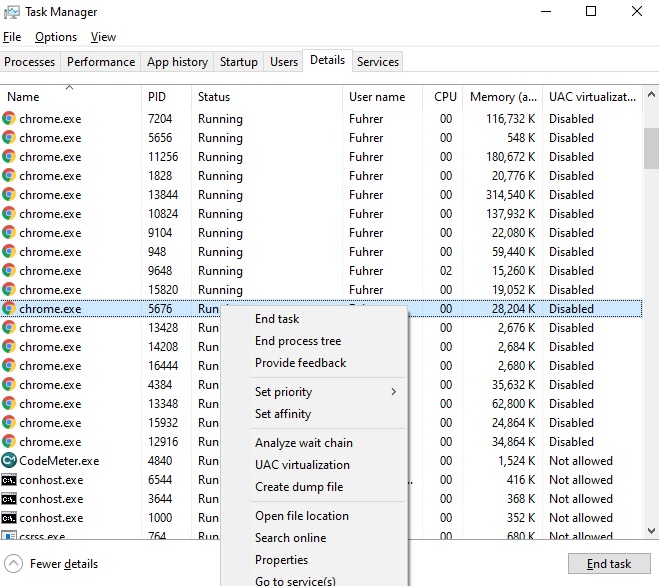
Let’s take a look at the options in this context menu:
- End task: This is the same option found on the Processes tab.
- End process tree: Terminating the process, and all the processes created by the process.
- Set priority: Setting a priority for the process: Low, Below normal, Normal, Above normal, High, and Realtime. Processes start at normal priority. Lower priority is ideal for background processes, and higher priority is ideal for desktop processes.
- Set affinity: Setting the processor affinity of a process. By default, processes run on all processors in a system. You can use this to limit a process to a particular processor.
- Analyze wait chain: View what threads in the processes are waiting for. This shows you which processes and threads are waiting to use a resource used by another process, and is a useful debugging tool for programmers to diagnose hangs.
- UAC virtualization: Enable or disable User Account Control virtualization for a process. This feature fixes applications that require administrator access by virtualizing their access to system files, redirecting their file and registry access to other folders.
- Create dump file:This is the same option found on the Processes tab.
- Open file location: This option is useful if you want to know the location of the EXE file on your computer.
- Search online: Searching in the internet for this process or program.
- Properties: View the properties window of the process’s .exe file.
- Go to service(s): Show the services associated with the process on the Services tab.
Source: howtogeek.com and online-tech-tips.com
Services Tab
The Services tab shows a list of the system services on your Windows system. These are background tasks that Windows runs, even when no user account is signed in. They’re controlled by the Windows operating system.
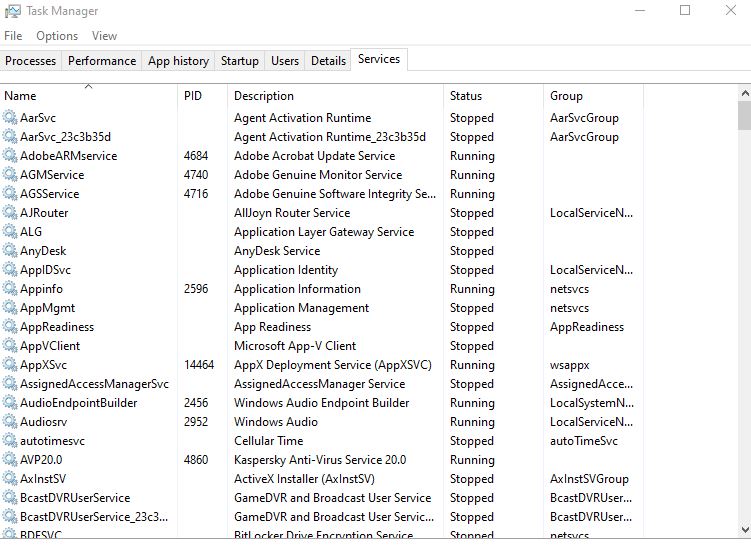
Many services are part of Windows itself. (Like Windows Update service downloads updates) but other services are installed by third-party programs or other Microsoft products (like SQL services).
You can right-click on a running service and select stop or restart in the menu that appears. In the same way, you can right-click on the service that is in the stop status and select the start option.
The only other noteworthy thing about this tab is that there is a column in this tab called Group. The group the service is in, if applicable. Windows loads one service group at a time at startup. A service group is a collection of similar services that are loaded as a group. In fact, in this tab we can apply almost the same management on all services as in the services console. There are a variety of ways to run services console, one of which is to enter “services.msc” in the run box and then press the enter button.
Sources:



















