In this post we are going to talk about Administrative Safeguard. This post is the second post in the HIPAA series. This series of posts is called the HIPAA Series.
The series will contain seven post:
- Security 101 for Covered Entities
- Security Standards: Administrative Safeguards
- Security Standards: Physical Safeguards
- Security Standards: technical Safeguards
- Security Standards- Organizational, Policies and Procedures and Documentation Requirements
- Basics of Risk Analysis and Risk Management
- Implementation for the Small Provider
But this series also has two spin offs. We suggest that if you do not have basic information about HIPAA, before starting this series, first read the following two posts:
Note, In across of this post:
(R)= Required, (A)= Addressable
—————————–
Source:
This article is a summary from of the hhs.gov website. With the following link:
Security Standards: Administrative Safeguards
For more info please refer to hhs.gov
Security Standards: Administrative Safeguards
It should be noted that HIPAA compliance has several main rules. One of them is the security rule. The security rule has three safeguards:
- Administrative Safeguard
- Physical Safeguard
- Technical Safeguard
This post is devoted to the standards for Administrative Safeguards and their implementation specifications and assumes the reader has a basic understanding of the Security Rule.
EPHI is to implement reasonable and appropriate administrative safeguards that establish the foundation for a covered entity’s security program. The objectives of this paper are to:
- Reviewing each Administrative Safeguards standard and implementation specification listed in the Security Rule.
- Discussing the purpose for each standard.
- Providing sample questions that covered entities may want to consider when implementing the Administrative Safeguards.
The Security Rule defines administrative safeguards as, “administrative actions, and policies and procedures, to manage the selection, development, implementation, and maintenance of security measures to protect electronic protected health information and to manage the conduct of the covered entity’s workforce in relation to the protection of that information.”
Administrative Safeguards includes nine standards, all of which we will discuss. These standards include:
Security Risk Management – STANDARD § 164.308(a) (1)
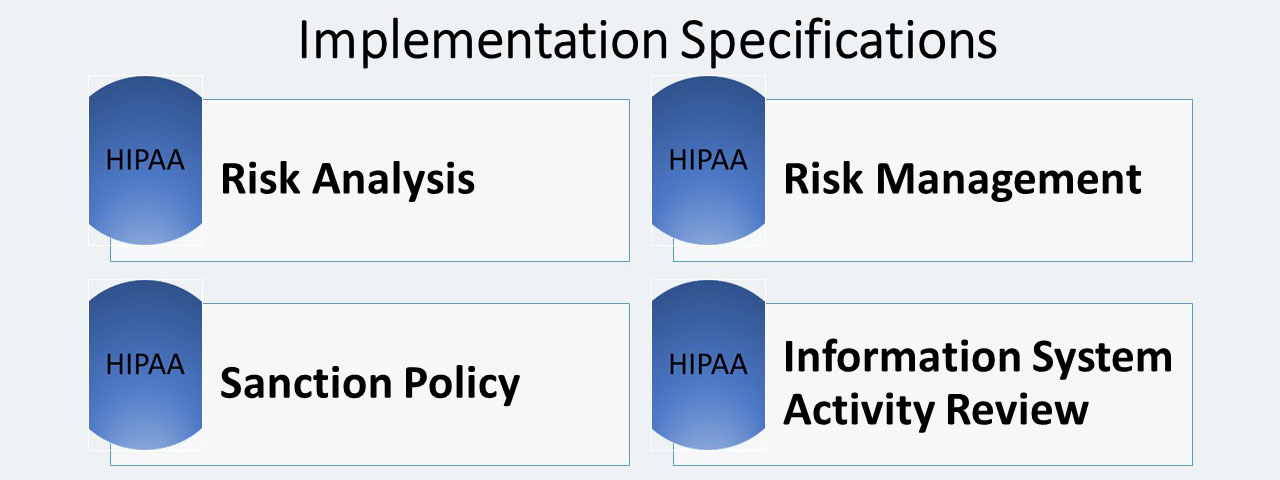
The first standard under Administrative Safeguards section is the Security Management Process. There are four implementation specifications (All required) in the Security Management Process standard:
The Importance of Risk Analysis and Risk Management
Risk analysis and risk management are standard information security processes that have already been adopted by some organizations within the health care industry.
- Risk Analysis: Conduct an accurate and thorough assessment of the potential risks and vulnerabilities to the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of electronic protected health information held by the covered entity the results from the risk analysis and risk management processes will become the baseline for security processes within covered entities.
- Risk Management: It is the process used to identify and implement security measures to reduce risk to a reasonable and appropriate level within the covered entity based on the covered entity’s circumstances.
Risk Analysis (R)
A risk analysis can be viewed as:
- The process of identifying potential security risks, and
- Determining the probability of occurrence and magnitude of risks.

Risk Management (R)
Implement security measures sufficient to reduce risks and vulnerabilities to a reasonable and appropriate level to comply with §164.306(a).

Sanction Policy (R)
Another implementation specification in the Security Management Process is the Sanction Policy. It requires covered entities to: “Apply appropriate sanctions against workforce members who fail to comply with the security policies and procedures of the covered entity.”

Information System Activity Review (R)
This review states that covered entities must: “Implement procedures to regularly review records of information system activity, such as audit logs, access reports, and security incident tracking reports.” Of course, information system activity review procedures may be different for each covered entity. The procedure should be customized to meet the covered entity’s risk management strategy and take into account the capabilities of all information systems with EPHI.

Assigned Security Responsibility- STANDARD § 164.308(a) (2)
The purpose of this standard is to identify who will be operationally responsible for assuring that the covered entity complies with the Security Rule.
There are no separate implementation specifications for this standard. The standard requires that covered entities: “Identify the security official who is responsible for the development and implementation of the policies and procedures required by this subpart [the Security Rule] for the entity.”
Covered entities should be aware of the following when assigning security responsibility:
- This requirement is comparable to the Privacy Rule standard at §164.530(a) (1), Personnel Designations.
- The Security Official and Privacy Official can be the same person, but are not required to be.
- While one individual must be designated as having overall responsibility, other individuals in the covered entity may be assigned specific security responsibilities.

Workforce Security- STANDARD § 164.308(a) (3)
This standard is states that covered entities must: “Implement policies and procedures to ensure that all members of its workforce have appropriate access to electronic protected health information, as provided under [the Information Access Management standard], and to prevent those workforce members who do not have access under [the Information Access Management standard] from obtaining access to electronic protected health information.”
For each workforce member, or job function, the covered entity must identify the EPHI that is needed, when it is needed, and make reasonable efforts to control access to the EPHI. This will also include identification of the computer systems and applications that provide access to the EPHI.
Within Workforce Security there are three addressable implementation specifications:
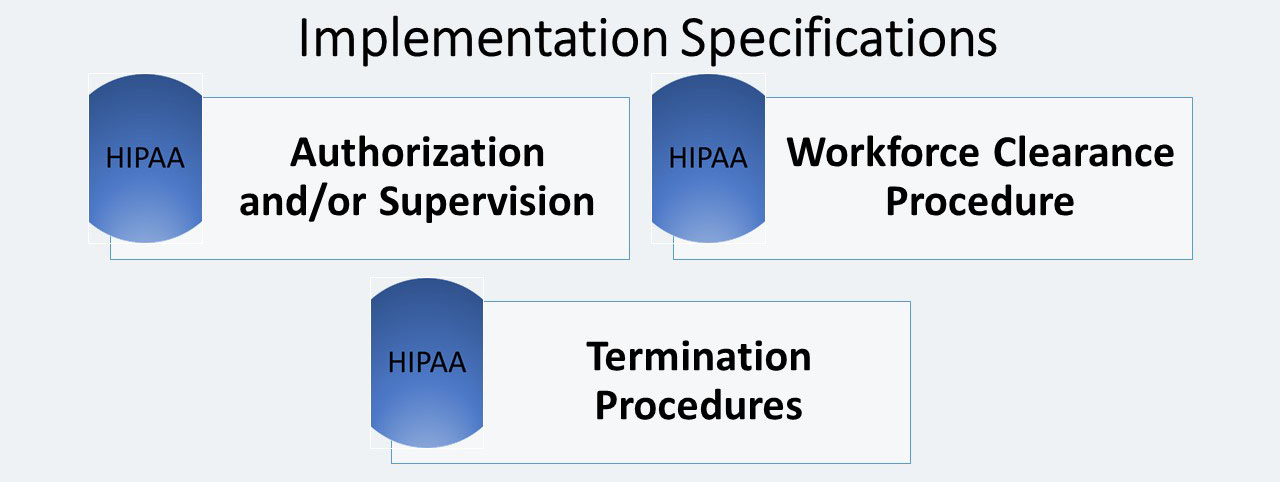
Authorization and/or Supervision (A)
Where the Authorization and/or Supervision implementation specification is a reasonable and appropriate safeguard for a covered entity, the covered entity must: “Implement procedures for the authorization and/or supervision of workforce members who work with electronic protected health information or in locations where it might be accessed.”
Authorization is the process of determining whether a particular user (or a computer system) has the right to carry out a certain activity, such as reading a file or running a program.
In a very small provider office, all staff members may need to access all EPHI in their information system, since they may perform multiple functions. In this case, the covered entity might document the reasons for implementing policies and procedures allowing this kind of global access.

Workforce Clearance Procedure (A)
The clearance process must establish the procedures to verify that a workforce member does in fact have the appropriate access for their job function. The covered entity must: “Implement procedures to determine that the access of a workforce member to electronic protected health information is appropriate.”

Termination Procedures (A)
- Termination procedures must be implemented to remove access privileges when an employee, contractor, or other individual previously entitled to access information no longer has these privileges.
- Whether the employee leaves the organization voluntarily or involuntarily, procedures to terminate access must be in place.
- The same process that is implemented for termination should also be used to change access levels if an employee’s job description changes to require more or less access to EPHI.

Information Access Management- STANDARD § 164.308(a)(4)
By implementing this standard, the risk of inappropriate disclosure, alteration, or destruction of EPHI is minimized. Covered entities are required to: “Implement policies and procedures for authorizing access to electronic
Protected health information that are consistent with the applicable requirements of subpart E of this part [the Privacy Rule].”
- Restricting access to only those persons and entities with a need for access is a basic tenet of security.
- Covered entities must determine those persons and/or entities that need access to EPHI within their environment.
The Information Access Management standard has three implementation specifications:
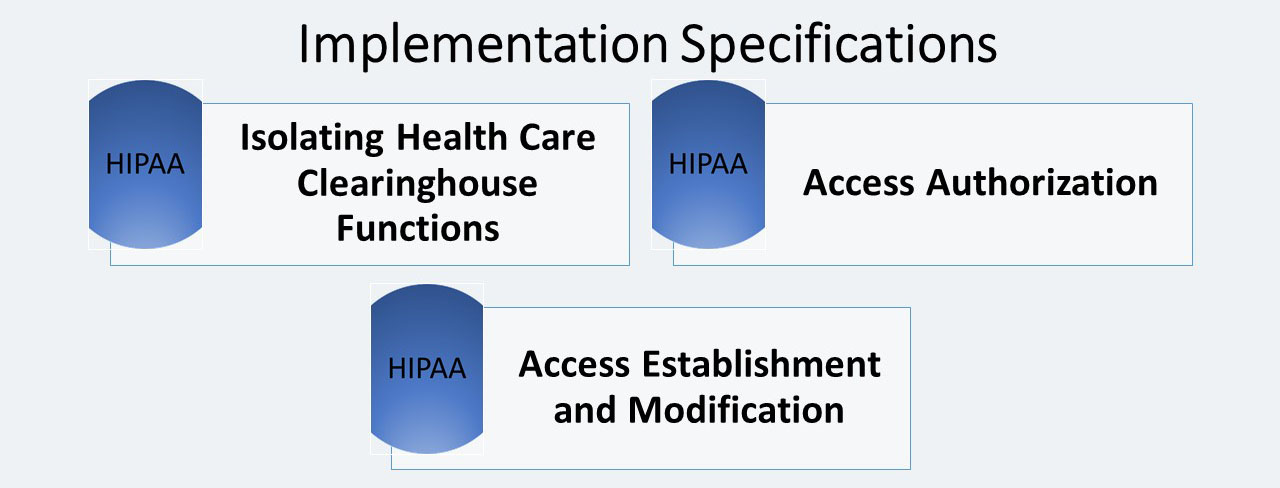
Isolating Health Care Clearinghouse Functions (R)
The Isolating Health Care Clearinghouse Functions implementation specification states: “If a health care clearinghouse is part of a larger organization, the clearinghouse must implement policies and procedures that protect the electronic protected health information of the clearinghouse from unauthorized access by the larger organization.”
This implementation specification only applies in the situation where a health care clearinghouse is part of a larger organization.

Access Authorization (A)
In safeguard for a covered entity, the covered entity must: “Implement policies and procedures for granting access to electronic protected health information, for example, through access to a workstation, transaction, program, process, or other mechanism.” A covered entity’s policies and procedures must identify who has authority to grant access privileges. It must also state the process for granting access. Then, covered entity must consider how access is established and modified.

Access Establishment and Modification (A)
A covered entity must: “Implement policies and procedures that, based upon the entity’s access authorization policies, establish, document, review, and modify a user’s right of access to a workstation, transaction, program, or process.” So, a covered entity must implement and manage the creation and modification of access privileges to workstations, transactions, programs or processes.

Security Awareness and Training – STANDARD § 164.308(a) (5)
Many security risks and vulnerabilities within covered entities are internal. This is why the next standard, Security Awareness and Training, is so important.
Safeguards will not protect the EPHI if the workforce is unaware of its role in adhering to and enforcing them. The Security Awareness and Training standard states that covered entities must: “Implement a security awareness and training program for all members of its workforce (including management).”
Security training for all new and existing members of the covered entity’s workforce is required by the compliance date of the Security Rule. In addition, periodic retraining should be given whenever environmental or operational changes affect the security of EPHI. Changes may include:
- New or updated policies and procedures
- New or upgraded software or hardware
- New security technology; or even changes in the Security Rule
The Security Awareness and Training standard has four implementation specifications.
Security Reminders (A)
The covered entity must implement periodic security updates.
There are many types of security reminders that covered entities may choose to implement:
- Notices in printed or electronic form
- Agenda items and specific discussion topics at monthly meetings
- Focused reminders posted in affected areas
- Formal retraining on security policies and procedures.
Protection from Malicious Software (A)
One important security measure that employees may need to be reminded of is security software that is used to protect against malicious software. So, covered entity, the covered entity must implement: “Procedures for guarding against, detecting, and reporting malicious software.”
Malicious software is frequently brought into an organization through email attachments, and programs that are downloaded from the Internet. Under the Security Awareness and Training standard, the workforce must also be trained regarding its role in protecting against malicious software, and system protection capabilities.
Login Monitoring (A)
A covered entity, the covered entity must implement: “Procedures for monitoring log-in attempts and reporting discrepancies.”
An inappropriate or attempted log-in is when someone enters multiple combinations of usernames and/or passwords to attempt to access an information system.
Fortunately, many information systems can be set to identify multiple unsuccessful attempts to log-in. Other systems might record the attempts in a log or audit trail. Still others might require resetting of a password after a specified number of unsuccessful log-in attempts.
Once capabilities are established the workforce must be made aware of how to use and monitor them.
Password Management (A)
The covered entity must implement: “Procedures for creating, changing, and safeguarding passwords.” Also, covered entities must train all users and establish guidelines for creating passwords and changing them during periodic change cycles.

Security Incident Procedures- STANDARD § 164.308(a) (6)
This standard states that covered entities must: “Implement policies and procedures to address security incidents.” Addressing security incidents is an integral part of the overall security program because even covered entities with detailed security policies and procedures and advanced technology will have security incidents.
The Security Rule defines a security incident as, “the attempted or successful unauthorized access, use, disclosure, modification, or destruction of information or interference with system operations in an information system.”
Whether a specific action would be considered a security incident, the specific process of documenting incidents, what information should be contained in the documentation, and what the appropriate response should be will be dependent upon an entity’s environment and the information involved.

Response and Reporting (R)
The covered entities must: “Identify and respond to suspected or known security incidents; mitigate, to the extent practicable, harmful effects of security incidents that are known to the covered entity; and document security incidents and their outcomes.”
Security incident procedures must describe how workforce members are to respond to an incident. This may include:
- Preserving evidence mitigating
- To the extent possible
- The situation that caused the incident
- Documenting the incident and the outcome
- Evaluating security incidents as part of ongoing risk management.
Covered entities must be aware of any number of possible incidents that they may have to deal with. For example:
- Stolen or otherwise inappropriately obtained passwords that are used to access EPHI
- Corrupted backup tapes that do not allow restoration of EPHI
- Virus attacks that interfere with the operations of information systems with EPHI
- Physical break-ins leading to the theft of media with EPHI
- Failure to terminate the account of a former employee that is then used by an unauthorized user to access information systems with EPHI
- Providing media with EPHI, such as a PC hard drive or laptop, to another user who is not authorized to access the EPHI prior to removing the EPHI stored on the media.

Contingency Plan- STANDARD § 164.308(a) (7)
The purpose of contingency planning is to establish strategies for recovering access to EPHI should the organization experience an emergency or other occurrence, such as a power outage and/or disruption of critical business operations. The Contingency Plan standard requires that covered entities: “Establish (and implement as needed) policies and procedures for responding to an emergency or other occurrence (for example, fire, vandalism, system failure, and natural disaster) that damages systems that contain electronic protected health information.”
The Contingency Plan standard includes five implementation specifications.
Data Backup Plan (R)
The Data Backup Plan implementation specification requires covered entities to: “Establish and implement procedures to create and maintain retrievable exact copies of electronic protected health information.” Data Backup plans are an important safeguard for all covered entities, and a required implementation specification.

Disaster Recovery Plan (R)
The Disaster Recovery Plan implementation specification requires covered entities to: “Establish (and implement as needed) procedures to restore any loss of data.” Some covered entities may already have a general disaster plan that meets this requirement; however, each entity must review the current plan to ensure that it allows them to recover EPHI.

Emergency Mode Operation Plan (R)
This implementation specification requires covered entities to: “Establish (and implement as needed) procedures to enable continuation of critical business processes for protection of the security of electronic protected health information while operating in emergency mode.”

Testing and Revision Procedures (A)
The covered entity must: “Implement procedures for periodic testing and revision of contingency plans.” This implementation specification applies to all implementation specifications under the Contingency Plan standard, including the Data Backup Plan, Disaster Recovery Plan, and Emergency Mode Operations Plan.

Application and Data Criticality Analysis (A)
The covered entity must: “Assess the relative criticality of specific applications and data in support of other contingency plan components.” This implementation specification requires covered entities to identify their software applications (data applications that store, maintain or transmit EPHI) and determine how important each is to patient care or business needs, in order to prioritize for data backup, disaster recovery and/or emergency operations plans.
Evaluation- STANDARD § 164.308(a) (8)
Covered entities must implement ongoing monitoring and evaluation plans. Covered entities must periodically evaluate their strategy and systems to ensure that the security requirements continue to meet their organizations’ operating environments.
The Evaluation standard has no separate implementation specifications. The standard requires covered entities to: “Perform a periodic technical and nontechnical evaluation, based initially upon the standards implemented under this rule and subsequently, in response to environmental or operations changes affecting the security of electronic protected health information that establishes the extent to which an entity’s security policies and procedures meet the requirements of this subpart [the Security Rule].”

Business Associate Contracts and Other Arrangements- STANDARD § 164.308(b) (1)
The Business Associate Contracts and Other Arrangements standard states that: A covered entity may permit a business associate to create, receive, maintain, or transmit electronic protected health information on the covered entity’s behalf only if the covered entity obtains satisfactory assurances, in accordance with [the Organizational Requirements] that the business associate will appropriately safeguard the information (Emphasis added).
This standard is comparable to the Business Associate Contract standard in the Privacy Rule, but is specific to business associates that create, receive, maintain or transmit EPHI.
The Business Associate Contracts and Other Arrangements standard does not apply with respect to:
“(i) The transmission by a covered entity of EPHI to a health care provider concerning the treatment of an individual.
(ii) The transmission of EPHI by a group health plan or an HMO or health insurance issuer on behalf of a group health plan to a plan sponsor, to the extent that the requirements of § 164.314(b) and §
164.504(f) apply and are met; or
(iii) The transmission of EPHI from or to other agencies providing the services at § 164.502(e)(1)(ii)(C), when the covered entity is a health plan that is a government program providing public benefits, if the requirements of § 164.502(e)(1)(ii)(C) are met.”

Written Contract or Other Arrangement (R)
Covered entities are required to: “Document the satisfactory assurances required [the Business Associate Contracts and Other Arrangements] of this section through a written contract or other arrangement with the business associate that meets the applicable requirements of [the Organizational Requirements].”

—————————–
Source:
This article is a summary from of the hhs.gov website. With the following link:
Security Standards: Administrative Safeguards
For more info please refer to hhs.gov



















