Identification of Vulnerability & Threats
Identification of vulnerability & threats is one of most important the aspects of CISSP training course.
Vulnerability
A vulnerability is a weakness in a system or its design. Classifying vulnerabilities helps in identifying its impact on the system. Vulnerability greatly increases the risk of the organization’s assets.
Policy flaws
- Design errors
- Software vulnerabilities
- Protocol weaknesses
- Hardware vulnerabilities
- Misconfiguration
- Human factors
- Malicious software
- Physical access to network resources
Threat
The threat is meaning the possibility of an attack. In other words, a threat is any potential danger to an asset. Correct Configuring countermeasure of vulnerabilities reduces the threats to a system.
The entity that uses the vulnerability of the system is known as malicious actor and path used by this entity to launch an attack is known as a threat vector.
You can more read about identification of vulnerability & threats here.
Risk Assessment
Risk management determines how much an organization can accept uncertainty. A threat without any related vulnerability does not create any risk. Scoping the risk is the process of quantifying a threat possibility & its impact on an enterprise.
The process of risk identification occurs during a risk assessment.
Risk analysis is a process of assessment of risks, which allows the security professional to identify and catalog different risks, and then build a certain plan and technique to deal with these risks.
Enterprise Risk Management
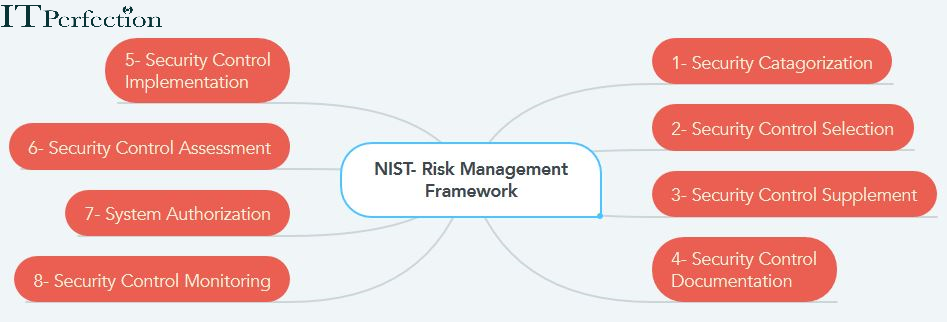
Enterprise Risk Management process by NIST includes the following steps:
- Categorize the information system (criticality/sensitivity)
- Select and tailor baseline (minimum) security controls
- Supplement the security controls based on risk assessment
- Document security controls in system security plan
- Implement the security controls in the information system
- Assess the security controls for effectiveness
- Authorize information system operation based on mission risk
- Monitor security controls on a continuous basis
Applicable Types of Controls
These controls check the reliability, and efficiency of managerial policies. Three types of controls are as follows:
- Preventive Control: The control designed for prevention means. For example, dividing the process of payment transaction into three step helps in reducing the chances of error.
- Detective Control: The control designed for troubleshooting or identifying errors, and issues. These controls are effective after an incident.
- Corrective Control: When troubleshooting, assessment or audit process of detective control to find any vulnerability, corrective control secures and reduces its impact. Corrective control includes enforcement of policies to restore a properly functioning system.
