Asset Security Domain Review
This domain focuses on protecting information assets. Information is the worthiest asset to an organization. The information’s value, determines the level of protection required by the organization. Asset security is one of most important the aspects of CISSP training course.
A data classification scheme helps an organization assign a value to its information assets based on its sensitivity to loss or disclosure and its criticality to the organization’s mission or purpose.
An organization’s employees need to understand the classification schema being used and proper destruction or disposal procedures.
Data Classification
The main purpose of data classification is to specify the level of confidentiality, integrity, and availability (CIA) protection required for each type of dataset. Classification of data helps implementing correct and effective security measures and control to protect the information assets efficiently.
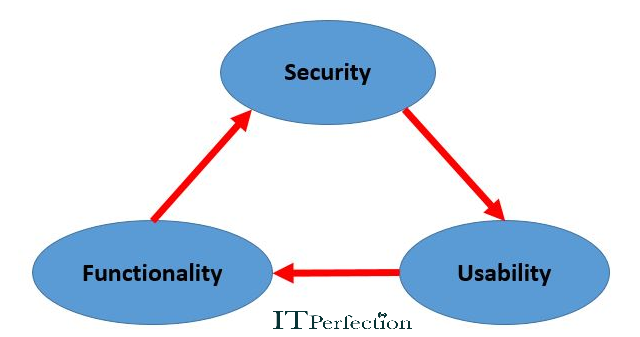
In a System, Level of Security is a measure of the strength of the Security in the system, Functionality, and Usability. These three components of a triangle must be balanced.
Commercial Data Classification
Criteria by which commercial data is classified include:
- Value: The most common classification criterion in commercial organizations.
- Age/useful life: Information that loses value over time, becomes obsolete or irrelevant, or becomes common/public knowledge is classified this way.
- Regulatory requirements: Private information, such as medical records
Data Classification Procedures
The standard steps for classifying data are as follows:
- Define classification levels
- Identify the criteria that determine the classification of data
- Identify data owners
- Identify the data custodians ( They are responsible for maintaining data and its security level)
- Indicate the security controls
- Document any exceptions
- Indicate the methods that can be used to transfer custody of the information to a different data owner
- Create a procedure to review the classification and ownership periodically
- Indicate procedures for declassifying the data.
- Integrate these issues into the security-awareness program
Classifications Levels
There are no specific rules for classifying the levels of data. The following can be considered as two proposed classifications:
- Data classification for commercial businesses
- Data classification for the military
- Data classification for the government
Each classification should have different procedures relating to how data is accessed, used, and destroyed. For example:
- Public: in this Classification, Disclosure is not acceptable.
- Private: It is appropriate to use the information of individuals in the organization.
- Sensitive: It is appropriate where a higher level of assurance of completeness and accuracy is required.
- Confidential: Personal information of personnel, programming codes of the organization’s proprietary software, military and government information. Confidential information is the lowest level of classified government information.
- Unclassified: Data that is insignificant or cannot be classified. (Maybe because they are not be structured)
- Sensitive but classified : like the medical data
- Secret: If disclosed, it could cause serious damage to national security or Organizational security.
- TOP Secret: If disclosed, it could be crucial damage to national
- security or organizational security.
Asset Classification
Asset classification depends on the CIA values.
- Confidentiality: Unauthorized users should not view the information.
- Integrity: Unauthorized users should not modify the information.
- Availability: Authorized users can access the information.
Parameters that are involved in an asset may include monetary value, intellectual property value, legal and regulatory requirements, privacy requirements and competitive advantage, and so on.
